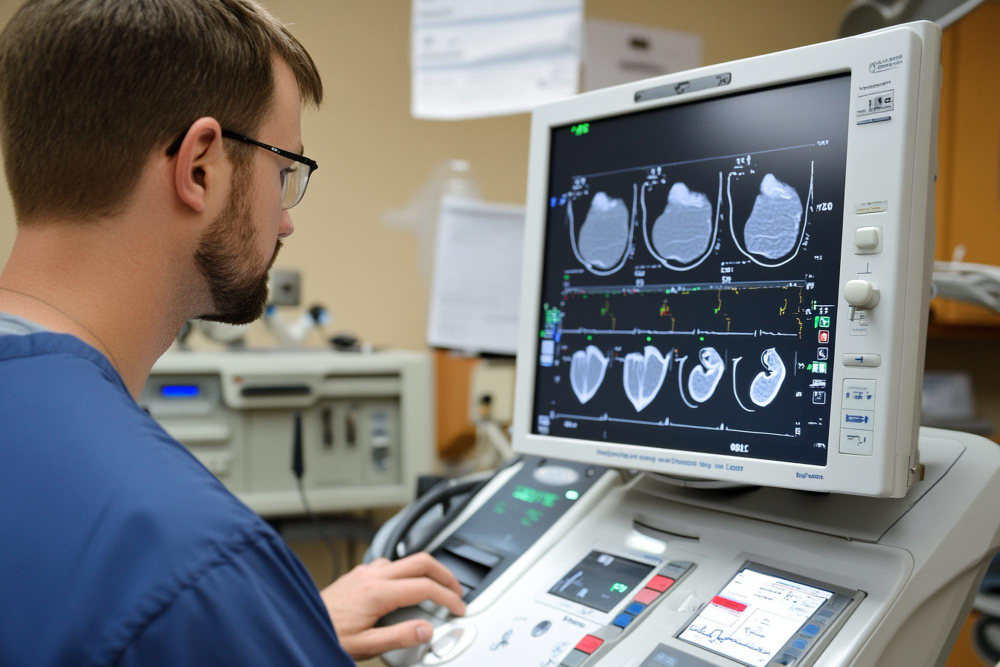
Echocardiography, also known as an “echo,” is a specialized ultrasound imaging technique that evaluates the structure and function of the heart. It uses high-frequency sound waves to create detailed images, providing crucial insights into cardiac health.